Have you ever wondered if heat can make your glass items unsafe? Whether it’s a window, a glass cup, or even a car windshield, understanding how heat affects glass is crucial for your safety.
You might think glass is strong and unbreakable, but the truth could surprise you. You’ll discover what really happens to glass when it gets hot, why it sometimes cracks or shatters, and how you can protect yourself and your belongings.
Keep reading—your safety depends on knowing these facts.
Credit: modernize.com
Heat And Glass Basics
Heat and glass have a complex relationship. Glass can handle some heat but not all types. Understanding how heat affects glass helps us keep safe in many situations. It also guides us in choosing the right glass for different uses.
Glass is not all the same. Different types of glass react differently to heat. Knowing these differences is important for safety and durability. Let’s explore the basics of heat and glass.
Types Of Glass And Heat Resistance
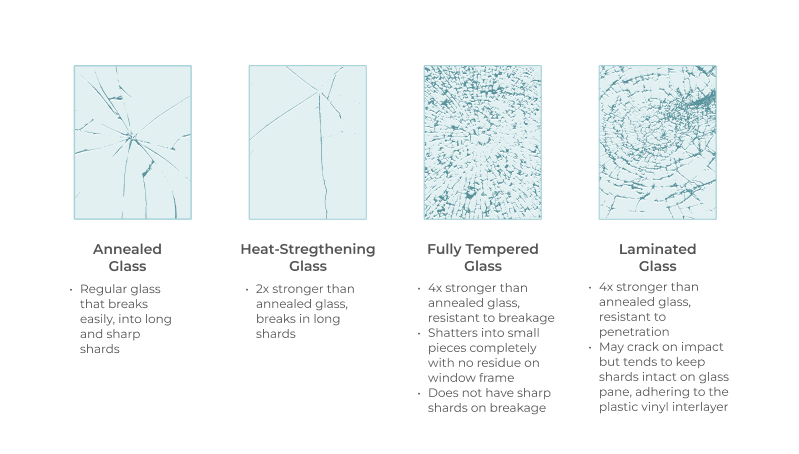
Common glass, like window glass, breaks easily under heat. It expands and cracks with quick temperature changes. Tempered glass is stronger and handles heat better. It heats and cools evenly to avoid breaking.
Borosilicate glass resists heat very well. It is used in cookware and lab glass. This glass can handle sudden heat without cracking. Laminated glass has layers that add strength and safety. It is often used in car windshields.
How Glass Responds To Temperature Changes
Glass expands when heated and shrinks when cooled. Fast temperature changes cause stress inside the glass. This stress can lead to cracks or breaks. Slow temperature changes allow the glass to adjust safely.
Heat causes some types of glass to soften or bend. Others stay hard but may still crack under pressure. The way glass reacts depends on its composition and thickness. Careful handling around heat can prevent accidents.

Credit: thebottledepot.co
Factors Influencing Glass Safety
Glass safety depends on several key factors. Heat can cause glass to behave in different ways. Understanding these factors helps prevent accidents. It also guides the right choice of glass for various uses.
Thermal Shock And Its Effects
Thermal shock occurs when glass heats unevenly. Hot spots create stress inside the glass. This stress can cause cracks or breaks. Rapid temperature changes increase the risk. Glass exposed to sudden heat is more fragile.
Glass Thickness And Composition
Thicker glass handles heat better than thin glass. Composition matters too. Some glass types resist heat and stress more. Tempered and laminated glass provide extra strength. These types reduce the chance of breaking under heat.
Role Of Coatings And Treatments
Coatings protect glass from heat damage. Some coatings reflect heat away from the surface. Treatments can strengthen the glass structure. These layers improve durability and safety. They help glass last longer in hot conditions.
Common Risks From Heat Exposure
Heat can harm glass in many ways. High temperatures cause stress inside the glass. This stress creates risks that affect safety and durability. Knowing these risks helps protect glass in homes and buildings.
Cracking And Shattering Causes
Glass cracks when it heats unevenly. One part gets hot faster than another. This difference causes tension inside the glass. If the tension is too strong, the glass breaks.
Sudden temperature changes increase the chance of shattering. For example, pouring hot water on cold glass can cause cracks. Sunlight heating one side of a window and cold air cooling the other side also creates cracks.
Impact On Structural Integrity
Heat weakens the strength of glass. Over time, repeated heating and cooling cause small damages inside. These damages grow and reduce the glass’s ability to hold weight.
Weak glass can fail during storms or accidents. This failure risks injury and property damage. Heat exposure can shorten the life of glass in windows, doors, and other structures.
Testing Glass For Heat Safety
Testing glass for heat safety is important for many uses. Glass can break or crack under high heat. This can cause safety risks. Testing shows if glass can handle heat well. It helps manufacturers make stronger glass. It also helps buyers choose safe products.
Different types of glass need different tests. Some glass is made for ovens or windows. Other glass goes in cars or buildings. Each type must meet certain heat safety rules. Testing checks if glass meets these rules.
Industry Standards And Certifications
Industry standards guide how to test glass for heat. These rules come from safety organizations worldwide. They set clear limits for heat resistance. Glass that meets these rules gets special certificates. These certificates prove glass is safe to use. Builders and buyers trust these marks. They show the glass passed tough tests.
Methods For Heat Resistance Testing
Testing methods include heating and cooling glass quickly. This checks if glass can survive sudden temperature changes. Another test heats glass slowly to a set point. Experts look for cracks or breaks. Some tests use machines to apply heat evenly. Others check how glass handles long heat exposure. Each test gives useful data on glass strength. This helps improve glass safety for many uses.
Practical Tips For Heat Safety
Heat affects glass safety in many ways. Knowing how to handle glass around heat helps prevent cracks and breaks. This section shares practical tips for keeping glass safe when exposed to heat. These tips apply to kitchens, appliances, and installation processes.
Safe Usage In Kitchens And Appliances
Glass in kitchens faces heat from ovens, stoves, and microwaves. Use heat-resistant glass designed for cooking. Avoid placing hot glass on cold surfaces. Sudden temperature changes cause glass to shatter. Use trivets or heat pads under hot glass items. Keep glass away from direct flames or heating elements. Clean glass regularly to prevent buildup that weakens it.
Handling And Installation Guidelines
Handle glass with care to avoid stress points. Wear gloves to prevent slipping and cuts. Install glass according to manufacturer instructions for heat exposure. Use proper seals and gaskets to allow expansion. Avoid forcing glass into frames that are too small. Check for chips or cracks before installation. Damaged glass is more likely to break under heat.
Preventing Heat-related Damage
Protect glass from rapid temperature changes. Gradually heat or cool glass surfaces. Avoid placing hot pots directly on glass tables. Use protective films or coatings to increase heat resistance. Inspect glass regularly for signs of stress or damage. Replace glass if it shows any weakness. Keep heat sources at a safe distance from glass fixtures.

Credit: www.amazon.com
Innovations In Heat-resistant Glass
Heat can cause ordinary glass to break or crack easily. Innovations in heat-resistant glass help prevent this problem. These new types of glass keep safety and strength even under high temperatures. They are used in buildings, cars, and many other places to protect people and property.
Heat-resistant glass is made to handle sudden temperature changes. It does not shatter into sharp pieces like regular glass. This makes it safer in many environments. Advances in materials and production techniques make these glasses stronger and more reliable.
Tempered And Laminated Glass Features
Tempered glass is heated and cooled quickly to increase strength. It can stand high heat without breaking. If it does break, it turns into small, rounded pieces. This reduces injury risk.
Laminated glass has a plastic layer between two glass sheets. This layer holds the glass pieces together if broken. It also blocks heat and UV rays. Laminated glass keeps its shape even after damage.
Emerging Technologies
New heat-resistant glass uses special coatings to reflect heat. These coatings keep the glass cool and protect interiors. Some glass types use ceramic layers for better heat resistance.
Researchers develop glass with nanoparticles to improve strength. These tiny particles help glass resist heat and impacts. Smart glass technology also changes its properties based on temperature.
These innovations make glass safer and more useful in hot environments. They help protect people, reduce energy use, and increase comfort.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Heat Cause Glass To Break Easily?
Heat can cause glass to expand and contract, leading to stress. Sudden temperature changes increase the risk of breaking. Tempered or heat-resistant glass reduces breakage. Proper handling minimizes heat-related damage.
How Does Heat Affect Glass Safety?
Heat can weaken glass by creating internal stress. This stress may cause cracks or shattering. Safety glass types resist heat better. Avoid exposing glass to extreme or sudden temperature changes.
Can Glass Withstand High Temperatures Safely?
Some glass types, like borosilicate, withstand high heat safely. Regular glass may crack or shatter under high heat. Always check glass specifications before heat exposure to ensure safety.
What Is Thermal Shock In Glass?
Thermal shock occurs when glass faces rapid temperature changes. It causes uneven expansion, leading to cracks or breaks. Using tempered glass helps prevent thermal shock damage. Avoid sudden heat or cold exposure.
Conclusion
Heat can change the safety of glass in many ways. Some glass types handle heat well, while others break easily. Knowing which glass to use helps prevent accidents. Always choose glass made for heat resistance in hot places. Small cracks or chips can grow with heat stress.
Regular checks keep glass safe and strong. Simple care and the right glass keep homes and workplaces secure. Understanding heat’s effect on glass helps protect people every day. Safety matters most when glass meets heat.

Leave a Reply